Flagsmith JavaScript SDK
This library can be used with pure JavaScript, React (and all other popular frameworks/libraries) and React Native projects. The source code for the client is available on Github.
Example applications for a variety of JavaScript frameworks such as React, Vue and Angular, as well as React Native, can be found here:
Installation
NPM
We also have flagsmith-es if you'd prefer to use ES modules.
npm i flagsmith --save
NPM for React Native
The ReactNative SDK shares the exact same implementation of Flagsmith, however, the defaults for some underlying libraries (e.g. AsyncStorage) use React Native compatible implementations.
npm i react-native-flagsmith --save
Via JavaScript CDN
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/flagsmith/index.js"></script>
Basic Usage
The SDK is initialised against a single environment within a project on https://flagsmith.com, for example the Development or Production environment. You can find your Client-side Environment Key in the Environment settings page.
Example: Initialising the SDK
import flagsmith from 'flagsmith or react-native-flagsmith'; //Add this line if you're using flagsmith via npm
flagsmith.init({
environmentID: '<YOUR_CLIENT_SIDE_ENVIRONMENT_KEY>',
// api:"http://localhost:8000/api/v1/" set this if you are self hosting, and point it to your API
cacheFlags: true, // stores flags in localStorage cache
enableAnalytics: true, // See https://docs.flagsmith.com/flag-analytics/ for more info
onChange: (oldFlags, params) => {
//Occurs whenever flags are changed
const { isFromServer } = params; //determines if the update came from the server or local cached storage
//Check for a feature
if (flagsmith.hasFeature('my_cool_feature')) {
myCoolFeature();
}
//Or, use the value of a feature
const bannerSize = flagsmith.getValue('banner_size');
//Check whether value has changed
const bannerSizeOld = oldFlags['banner_size'] && oldFlags['banner_size'].value;
if (bannerSize !== bannerSizeOld) {
// Do something!
}
},
});
Providing Default Flags
You can define default flag values when initialising the SDK. This ensures that your application works as intended in the event that it cannot receive a response from our API.
import flagsmith from 'flagsmith or react-native-flagsmith'; //Add this line if you're using flagsmith via npm
flagsmith.init({
environmentID: '<YOUR_CLIENT_SIDE_ENVIRONMENT_KEY>',
defaultFlags: {
feature_a: { enabled: false},
font_size: { enabled: true, value: 12 },
}
onChange: (oldFlags, params) => {
...
},
});
Providing Default Flags as part of CI/CD
You can automatically set default flags for your frontend application in CI/CD by using our CLI in your build pipelines.
The main steps to achieving this are as follows:
-
Install the CLI
npm i flagsmith-cli --save-dev -
Call the CLI as part of npm postinstall to create a
flagsmith.jsoneach time you runnpm install. This can be done by either:- Using an environment variable
export FLAGSMITH_ENVIRONMENT=<YOUR_CLIENT_SIDE_ENVIRONMENT_KEY> flagsmith get - Manually specifying your environment key
flagsmith get <YOUR_CLIENT_SIDE_ENVIRONMENT_KEY>.
- Using an environment variable
-
In your application, initialise Flagsmith with the resulting JSON, this will set default flags before attempting to use local storage or call the API.
flagsmith.init({environmentID: json.environmentID, state:json})
A working example of this can be found here. A list of cli commands can be found here.
Identifying users
Identifying users allows you to target specific users from the Flagsmith dashboard and configure features and traits. You can call this before or after you initialise the project, calling it after will re-fetch features from the API.
You can identify the users as part of initialising the client or after with the function flagsmith.identify.
User features can be managed by navigating to users on https://flagsmith.com for your desired
project. 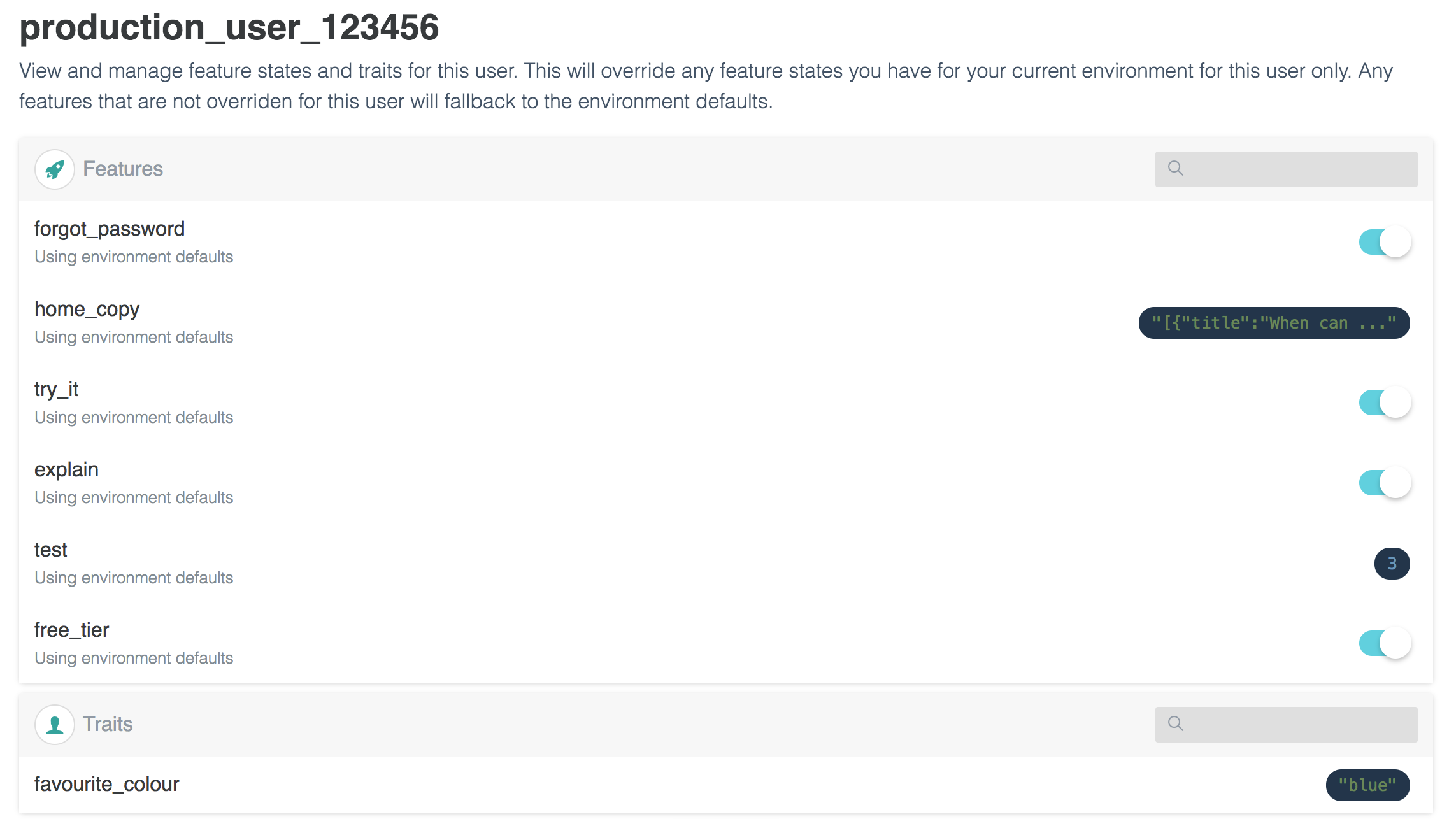
Example: Identifying a user after initialising the client
When you initialise the client without an identity, it will fetch the flags for a given environment (unless you provide
preventFetch:true).
import flagsmith from 'flagsmith';
flagsmith.init({
environmentID: '<YOUR_CLIENT_SIDE_ENVIRONMENT_KEY>',
onChange: (oldFlags, params) => {
//Occurs whenever flags are changed
const { isFromServer } = params; //determines if the update came from the server or local cached storage
//Set a trait against the Identity
flagsmith.setTrait('favourite_colour', 'blue'); //This save the trait against the user, it can be queried with flagsmith.getTrait
//Check for a feature
if (flagsmith.hasFeature('my_power_user_feature')) {
myPowerUserFeature();
}
//Check for a trait
if (!flagsmith.getTrait('accepted_cookie_policy')) {
showCookiePolicy();
}
//Or, use the value of a feature
const myPowerUserFeature = flagsmith.getValue('my_power_user_feature');
//Check whether value has changed
const myPowerUserFeatureOld = oldFlags['my_power_user_feature'] && oldFlags['my_power_user_feature'].value;
if (myPowerUserFeature !== myPowerUserFeatureOld) {
// Do something!
}
},
});
/*
Can be called either after you're done initialising the project or in flagsmith.init with its identity and trait properties
to prevent flags being fetched twice.
*/
flagsmith.identify('flagsmith_sample_user'); //This will create a user in the dashboard if they don't already exist
Example: Initialising the SDK with a user
Initialising the client with an identity property will retrieve the user's flags instead of the environment defaults. You can also specify traits at this point which could determine the flags that come back based on segment overrides.
import flagsmith from 'flagsmith';
flagsmith.init({
environmentID: '<YOUR_CLIENT_SIDE_ENVIRONMENT_KEY>',
identity: 'flagsmith_sample_user',
traits: { age: 21, country: 'England' }, // these will add to the user's existing traits
onChange: (oldFlags, params) => {
//Occurs whenever flags are changed
const { isFromServer } = params; //determines if the update came from the server or local cached storage
//Set a trait against the Identity
flagsmith.setTrait('favourite_colour', 'blue'); //This save the trait against the user, it can be queried with flagsmith.getTrait
//Check for a feature
if (flagsmith.hasFeature('my_power_user_feature')) {
myPowerUserFeature();
}
//Check for a trait
if (!flagsmith.getTrait('accepted_cookie_policy')) {
showCookiePolicy();
}
//Or, use the value of a feature
const myPowerUserFeature = flagsmith.getValue('my_power_user_feature');
//Check whether value has changed
const myPowerUserFeatureOld = oldFlags['my_power_user_feature'] && oldFlags['my_power_user_feature'].value;
if (myPowerUserFeature !== myPowerUserFeatureOld) {
}
},
});
API Reference
All function and property types can be seen here.
Initialisation options
| Property | Description | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
environmentID: string | Defines which project environment you wish to get flags for. example ACME Project - Staging. | YES | null |
onChange?: (previousFlags:IFlags, params:IRetrieveInfo, loadingState:LoadingState)=> void | Your callback function for when the flags are retrieved (previousFlags,{isFromServer:true/false,flagsChanged: true/false, traitsChanged:true/false})=>{...} | YES | null |
onError?: (res:{message:string}) => void | Callback function on failure to retrieve flags. (error)=>{...} | null | |
realtime?:boolean | Whether to listen for Real Time Flag events | false | |
asyncStorage?:any | Needed for cacheFlags option, used to tell the library what implementation of AsyncStorage your app uses, i.e. ReactNative.AsyncStorage vs @react-native-community/async-storage, for web this defaults to an internal implementation. | null | |
cacheFlags?: boolean | Any time flags are retrieved they will be cached, flags and identities will then be retrieved from local storage before hitting the API (see cache options) | null | |
cacheOptions?: \{ttl?:number, skipAPI?:boolean\} | A ttl in ms (default to 0 which is infinite) and option to skip hitting the API in flagsmith.init if there's cache available. | {ttl:0, skipAPI:false} | |
enableAnalytics?: boolean | Enable sending flag analytics for getValue and hasFeature evaluations. | false | |
enableLogs?: boolean | Enables logging for key Flagsmith events | null | |
defaultFlags?: {flag_name: {enabled: boolean, value: string,number,boolean}} | Allows you define default features, these will all be overridden on first retrieval of features. | null | |
preventFetch?: boolean | If you want to disable fetching flags and call getFlags later. | false | |
state?: IState | Set a predefined state, useful for SSR / isomorphic applications. | false | |
api?: string | Use this property to define where you're getting feature flags from, e.g. if you're self hosting. | https://edge.api.flagsmith.com/api/v1/ | |
eventSourceUrl?: string | Use this property to define where you're getting real-time flag update events (server sent events) from, e.g. if you're self hosting. | https://edge.api.flagsmith.com/api/v1/ | |
identity?: string | Specifying an identity will fetch flags for that identity in the initial API call. | YES | null |
traits?:Record<string, string or number or boolean> | Specifying traits will send the traits for that identity in the initial API call. | YES | null |
Available Functions
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
init(initialisationOptions)=> Promise<void> | Initialise the sdk against a particular environment |
hasFeature(key:string)=> boolean | Get the value of a particular feature e.g. flagsmith.hasFeature("powerUserFeature") // true |
getValue<T=string|number|boolean|null>(key:string,{ json?:boolean, fallback?:T })=> string|number|boolean | Get the value of a particular feature e.g. flagsmith.getValue("font_size", { fallback: 12 }) // 10, specifying json:true will automatically parse the value as JSON. |
getTrait(key:string)=> string|number|boolean | Once used with an identified user you can get the value of any trait that is set for them e.g. flagsmith.getTrait("accepted_cookie_policy") |
getAllTraits()=> Record<string,string|number|boolean> | Once used with an identified user you can get a key value pair of all traits that are set for them e.g. flagsmith.getTraits() |
getState()=>IState | Retrieves the current state of flagsmith, useful in NextJS / isomorphic applications. flagsmith.getState() |
setTrait(key:string, value:string|number|boolean)=> Promise<IFlags> | Once used with an identified user you can set the value of any trait relevant to them e.g. flagsmith.setTrait("accepted_cookie_policy", true) |
setTraits(values:Record<string, string|number|boolean>)=> Promise<IFlags> | Set multiple traits e.g. flagsmith.setTraits({foo:"bar",numericProp:1,boolProp:true}). Setting a value of null for a trait will remove that trait. |
incrementTrait(key:string, value:number)=> Promise<IFlags> | You can also increment/decrement a particular trait them e.g. flagsmith.incrementTrait("click_count", 1) |
startListening(ticks=1000:number)=>void | Poll the api for changes every x milliseconds |
stopListening()=>void | Stop polling the api |
getFlags()=> Promise<IFlags> | Trigger a manual fetch of the environment features, if a user is identified it will fetch their features. Resolves a promise when the flags are updated. |
identify(userId:string, traits?:Record<string, string or number or boolean>)=> Promise<IFlags> | Identify as a user, optionally with traits e.g. {foo:"bar",numericProp:1,boolProp:true}. This will create a user for your environment in the dashboard if they don't exist, it will also trigger a call to getFlags(), resolves a promise when the flags are updated. |
logout()=>Promise<IFlags> | Stop identifying as a user, this will trigger a call to getFlags() |
Multiple SDK Instances
Version 1.5 and above allows you to create multiple instances of the Flagsmith SDK. This may be used when you wish to identify multiple users simultaneously within your app and retain access to getValue, hasFeature etc for each user.
Type:
export function createFlagsmithInstance (): IFlagsmith
Usage:
import { createFlagsmithInstance } from 'flagsmith';
const flagsmith = createFlagsmithInstance();
const flagsmithB = createFlagsmithInstance();
// now you can use flagsmith as before but in its own instance
Flagsmith Loading State
Version 3.19 and above allows you to determine
the current loading state of the SDK and whether its current data is from default flags, cache or the API. Flagsmith
loading state can be accessed via the onChange event and the
useFlagsmithLoading() hook in the React SDK. The expected type of Flagsmith
loading state is as follows:
export declare enum FlagSource {
'NONE' = 'NONE',
'DEFAULT_FLAGS' = 'DEFAULT_FLAGS',
'CACHE' = 'CACHE',
'SERVER' = 'SERVER',
}
export declare type LoadingState = {
error: Error | null; // Current error, resets on next attempt to fetch flags
isFetching: bool; // Whether there is a current request to fetch server flags
isLoading: bool; // Whether any flag data exists
source: FlagSource; //Indicates freshness of flags
};
JSON Feature Values
The Flagsmith JavaScript client supports JSON remote config / feature values. When calling flagsmith.getValue,
specifying json:true will attempt to parse the feature value as JSON, it will fallback to fallback failing to parse
it.
const json = flagsmith.getValue('json_value', {
json: true,
fallback: { foo: null, bar: null },
});
TypeScript Support
Flagsmith has full TypeScript support for its JavaScript clients, you can find our main type definition file here. You can also enforce type safety of feature and trait names using generics:
Given that we type our flags and traits:
type FlagOptions = 'font_size' | 'hero';
type TraitOptions = 'example_trait';
We can now enforce these types:
// enforces you passing the correct key to flagsmith.getValue(flag:FlagOptions), flagsmith.getTrait(trait:TraitOptions)
import flagsmith from 'flagsmith';
const typedFlagsmith = flagsmith as IFlagsmith<FlagOptions, TraitOptions>;
// Similarly for the useFlagsmith hook is typed with useFlagsmith(flags:FlagOptions[],traits:TraitOptions[])
const flagsmith = useFlagsmith<FlagOptions, TraitOptions>(); // enforces flagsmith.getValue()
// for useFlags this will ensure you only can pass correct keys also
const flags = useFlags<FlagOptions, TraitOptions>(['font_size'], ['example_trait']);
// for getting JSON values this will type the return
const json = flagsmith.getValue<{ foo: string | null; bar: string | null }>('json_value', {
json: true,
fallback: { foo: null, bar: null },
});
console.log(json.foo); // typed as {foo: string|null, bar: string|null}
// If a type is not specified for getValue it will asume it from the type of fallback. In this case, a number.
const font_size = flagsmith.getValue('font_size', { fallback: 12 });
Datadog RUM JavaScript SDK Integration
This feature is still in beta with Datadog. Contact your Datadog representative before enabling the integration below.
The Flagsmith JavaScript SDK can be configured so that feature enabled state and remote config can be stored as
Datadog RUM feature flags
and user traits can be stored as
Datadog user session properties.
The integration requires an initialised Datadog datadogRum client.
Step 1: Initialise your Datadog RUM SDK with the feature_flags experimental feature
To start collecting feature flag data, initialize the Datadog RUM SDK and configure the enableExperimentalFeatures initialization parameter with ["feature_flags"].
import { datadogRum } from '@datadog/browser-rum';
// Initialize Datadog Browser SDK
datadogRum.init({
enableExperimentalFeatures: ["feature_flags"],
...
});
Step 2: Initialise the Flagsmith SDK with configuring
Initialise the Flagsmith SDK with the datadogRum option. Optionally, you can configure the client so that Flagsmith traits are sent to Datadog via ``datadogRum.setUser()````.
import { datadogRum } from '@datadog/browser-rum';
...
// Initialize the Flagsmith SDK
flagsmith.init({
datadogRum: {
client: datadogRum,
trackTraits: true,
},
...
})
Step 3: What happens next
- Whenever flag values are evaluated in your code, they will be sent to Datadog as user events.
- If the option to send Traits is enabled, the Trait key/value pairs will be sent to Datadog when the SDK receives its Flags.
This will track remote config and feature enabled states as feature flags in the following format
flagsmith_value_<FEATURE_NAME> // remote config
flagsmith_enabled_<FEATURE_NAME> // enabled state
Additionally, the integration will also store Flagsmith traits against the Datadog user in the following format:
flagsmith_trait_<FEATURE_NAME> // remote config
You can find an example of this integration here.
Dynatrace JavaScript SDK Integration
The Flagsmith JavaScript SDK can be configured so that feature enabled state, remote config and user traits can be
stored as Dynatrace session properties. The integration requires a configured Dynatrace dtrum object that is already
set up.
Step 1: Pass enableDynatrace into flagsmith.init()
In order to configure the JavaScript SDK, you need to pass in an instance of dtrum.
// Initialize the Flagsmith SDK
flagsmith.init({
//...Initialisation properties,
enableDynatrace: true,
});
When setting enableDynatrace to true flagsmith.init, Flagsmith will send session properties corresponding to flag
enabled state, flag values and user traits via
dtrum.sendSessionProperties()
- flag enabled state sends as a shortString as
trueorfalsewith the prefixflagsmith_enabled_- example:
flagsmith_enabled_hero: "true"
- example:
- Remote config values sends as value with the prefix flagsmith value, this value will be a javaDouble for numeric
values and a shortString for any other.
- example:
flagsmith_value_font_size: 21,flagsmith_value_hero_colour: "blue"
- example:
- Remote config values sends as value with the prefix flagsmith value, this value will be a javaDouble for numeric
values and a shortString for any other.
- example:
flagsmith_trait_age: 21,flagsmith_trait_favourite_colour: "blue"
- example:
Step 2: Add the session properties to your Dynatrace application settings
As with any other Dynatrace session properties, you need to also define session properties within the RUM application settings.
You can also add these properties via the Dynatrace API.
Dynatrace Screenshots
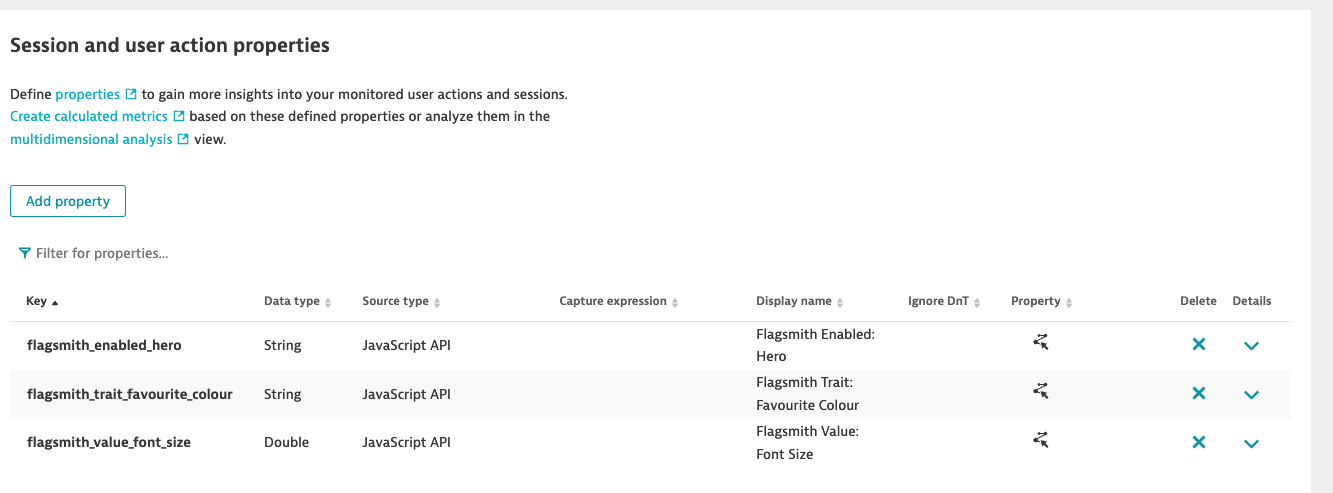
Defining Dynatrace Properties:
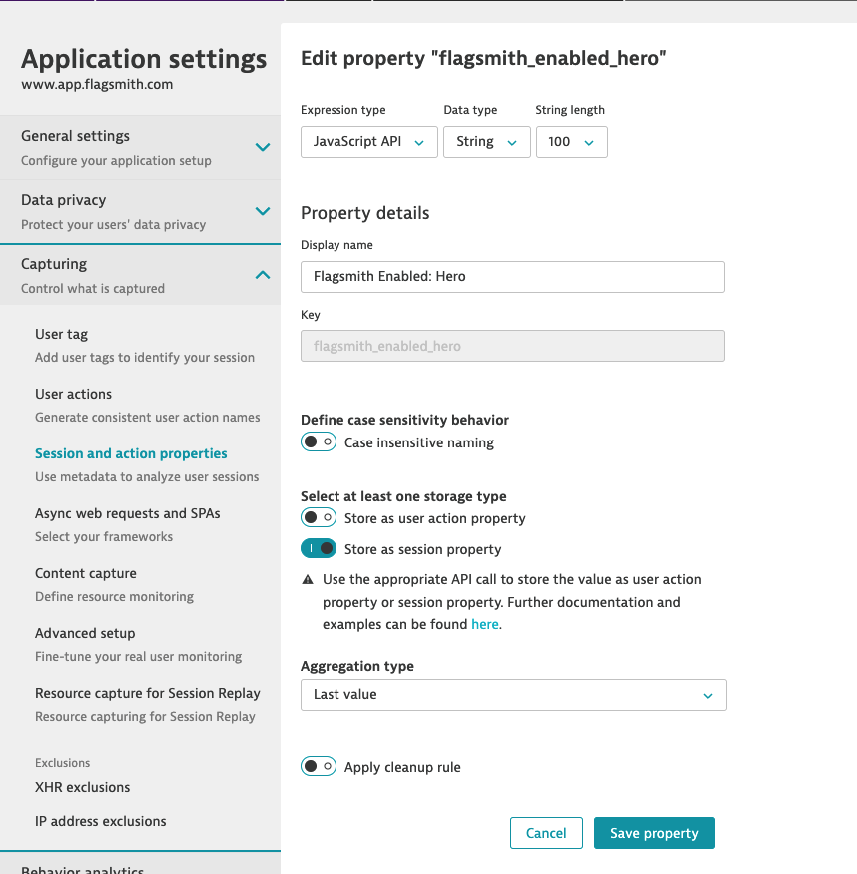
Defining a Flagsmith and Dynatrace Property:
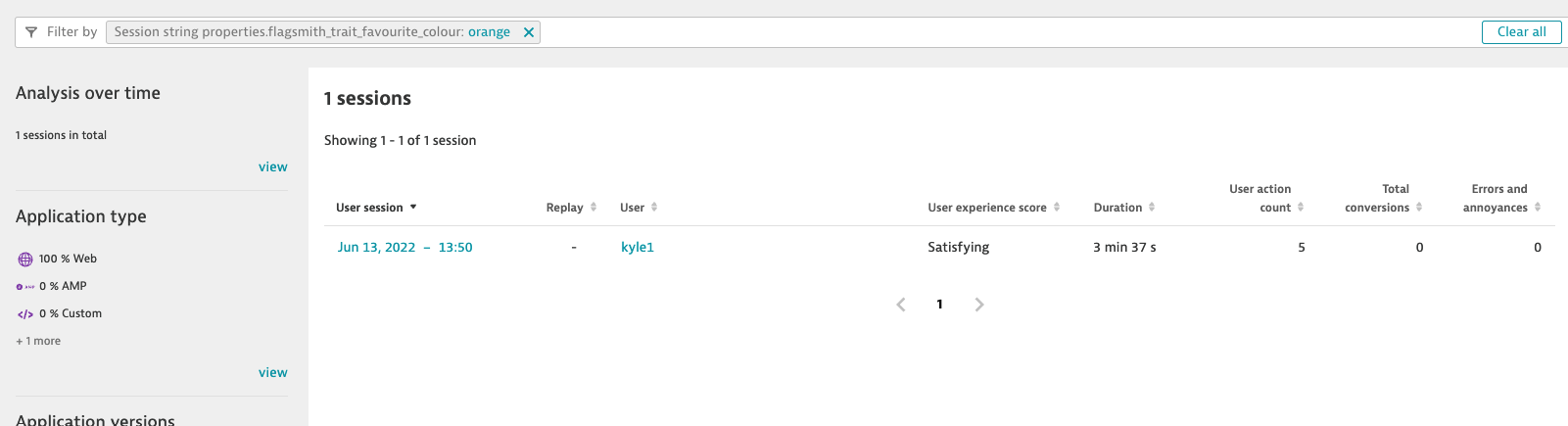
Filtering on a Flagsmith Flag:
FAQs
How do I call identify, setTraits etc alongside init?
initshould be called once in your application, we recommend you callinitbefore any other flagsmith call.initretrieves flags by default, you can turn this off with thepreventFetchoption toinit. This is useful for when you know you're identifying a user straight after.
When does onChange callback?
onChange calls when flags are fetched this can be a result of:
- init
- setTrait
- incrementTrait
- getFlags
- identify
- flags evaluated by local storage
Using onChange is best used in combination with your application's state management e.g. onChange triggering an action
to re-evaluate flags with hasFeature and getValue.
However, if this does not fit in with your development pattern, all the above flagsmith functions return a promise that resolves when fresh flags have been retrieved.
For example by doing the following:
await flagsmith.setTrait('age', 21);
const hasFeature = flagsmith.hasFeature('my_feature');
On change calls back with information telling you what has changed, you can use this to prevent any unnecessary re-renders.
onChange(this.oldFlags, {
isFromServer: true, // flags have come from the server or local storage
flagsChanged: deepEqualsCheck(oldFlags, newFlags),
traitsChanged: deepEqualsCheck(oldFlags, newFlags),
});
How does caching flags work?
If the cacheFlags is set to true on init, the SDK will cache flag evaluations in local async storage. Upon reloading
the browser, an onChange event will be fired immediately with the local storage flags. The flow for this is as follows
-
initis called -
if
cacheFlagsis enabled, local storage checks for any stored flags and traits. -
if flags have been found in local storage,
onChangeis triggered with the stored flags. -
at the same time, fresh flags will be retrieved which will result in another
onChangecallback. -
whenever flags have been retrieved local storage will be updated.
By default, these flags will be persisted indefinitely, you can clear this by removing "BULLET_TRAIN_DB" from
localStorage.
Why am I seeing ReferenceError: XMLHttpRequest is not defined?
The Flagsmith JavaScript client uses the fetch API to handle REST calls. Some frameworks such as Manifest and Nuxt do not support this out of the box.
In order to resolve this issue, you can provide a custom fetch implementation to the Flagsmith SDK. An example of this can be found here.